 Whether you refer to it as brown, chocolate, liver, or even sometimes red in certain breeds, B-Locus can sometimes be a confusing coat color test. Not only are there multiple B-Locus mutations that can each contribute to a brown coat color but they can also sometimes be found on the same gene copy making it even more confusing. So, let’s cover some basic biology on B-Locus mutations and hopefully alleviate the confusion.
Whether you refer to it as brown, chocolate, liver, or even sometimes red in certain breeds, B-Locus can sometimes be a confusing coat color test. Not only are there multiple B-Locus mutations that can each contribute to a brown coat color but they can also sometimes be found on the same gene copy making it even more confusing. So, let’s cover some basic biology on B-Locus mutations and hopefully alleviate the confusion.
B-Locus is very unique when it comes to genetic testing. All the other tests we offer have a single mutation that arose once in a single dog and has been carried to other dogs through breeding. The existence of different B-Locus mutations implies that the mutations most likely occurred separately in different dogs multiple times over dog breeding history. Some of the mutations can be found in many breeds such as the “bc”, “bd” and “bs” variants we test for in our classic B-Locus test. Other mutations arose in a specific breed such as the “ba” variant in Australian Shepherds, the “be” variant in Lancashire Heelers, or the “bh” variant in Siberian Huskies. There are still other breeds that have developed a separate mutation that has its own unique name such as CO-Locus or the Cocoa Locus in French bulldogs. But no matter the mutation, they all lead to a brown coat color and a brown nose.
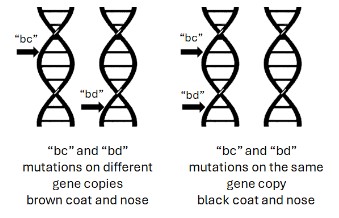
Since B-Locus mutations are recessive, it means a dog needs to inherit two copies of any of the B-Locus mutations to express a brown color in their coat. So, how is it possible for a dog to have a test result with two or more mutations but still be a black dog? The answer is that sometimes multiple mutations can be carried on the same gene copy and it is not currently possible to determine whether these mutations are carried on the same or different gene copy. We can only detect that they are present and by default, we have to assume they are on different gene copies. We have even found rare cases where a dog can have three B-Locus mutations. The only real way to differentiate whether mutations are carried on the same or different gene copies is to look at the dog’s nose. If the dog’s nose is brown, the mutations are present on different gene copies. If the dog’s nose is black, the mutations are present on the same gene copy and the dog should be considered a carrier for breeding purposes. The following diagram illustrates these two potential situations:
Understanding the complexities of B-Locus coat color testing will allow you to understand your genetic test result so you can make the appropriate breeding decisions. Be aware that different companies may offer tests that cover certain B-locus variants and not others and it’s important to know exactly what was tested for before making a final conclusion. Coat color in general can be complex and affected by other mutations in addition to B-Locus. We will cover the overall basics of coat color genetics in a future blog post. In the meantime, don’t hesitate to reach out if you have questions so we can help you plan your next breeding to get the coat color you want.

